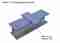
Large, seal welded overlapping surfaces require venting in the form of a hole(s) drilled in one of the overlapping surfaces. An enclosed area between overlapping surfaces may contain condensation or the welds may contain pin holes that will allow pre-treatment solutions to enter the enclosed area during the galvanizing process. This is unsafe when the articles are heated to 450°C in the molten zinc.
- Overlapping surfaces can be particularly dangerous if not designed correctly for galvanizing, so communication with the galvanizer is essential to ensure the correct venting is provided.
- Avoid narrow gaps between plates, overlapping surfaces, and back to back angles and channels, as fluid may get trapped leading to the possibility of an explosion or later corrosion of uncoated overlapped surfaces. See ‘For intermittent weld design’ for more information.
The general rules are:
- Overlapping surface areas under 10,000mm2 generally do not require venting.
- Overlapping surface areas between 10,000mm2 and 40,000mm2 shall be vented with a minimum Ø10mm vent hole.
- Above 40,000mm2 in overlapping surface area, the vent holes shall be minimum Ø12mm.
- When the overlapped surface area reaches 250,000mm2, vent holes shall be minimum Ø20mm and progressively placed every 250,000 mm2.

Alternatively, the use of intermittent welding can be considered, but is not preferred.
When overlaps are unavoidable:
- Seal edges using pinhole-free continuous welding and provide 2 vent holes for best outcomes.
- Pinholes from welding are very dangerous in articles to be galvanized and must be avoided.
- Size of the hole(s) should be equal to or greater than the steel thickness, with the minimum being 10mm.
- Avoid gaps between members or have at least a 2.5mm gap and stitch weld so all the surfaces can be galvanized. In this case, additional vent holes would not be required (see ‘For intermittent weld design’).
- Intermediate sized overlaps should be judged on the basis of weld integrity and residual welding heat in the joint to ensure total dryness at time of sealing.
- Longer or larger overlapping areas require spaced holes for progressive venting. Very large overlapping areas should be avoided as they are an undesirable design for galvanizing and are areas of high risk for crevice corrosion.
- The same principles used for general venting and draining should be used for location of vent holes in overlapping areas, i.e. in corners and diagonally opposite.
- There should be a flush fit-up of the items.
- Putting the hole through both sections can also be helpful.
For intermittent weld designs
The minimum space between the surfaces of the two components shall be at least 2.5mm.
This ensures:
- The overlapped area is self-venting.
- Avoids pre-treatment solutions being trapped in the gaps during the galvanizing process and seeping out over time.
- Allows all surfaces to be galvanized.